Structural Triangulation: A Closed-Form Solution to Constrained 3D Human Pose Estimation
ECCV 2022
Abstract
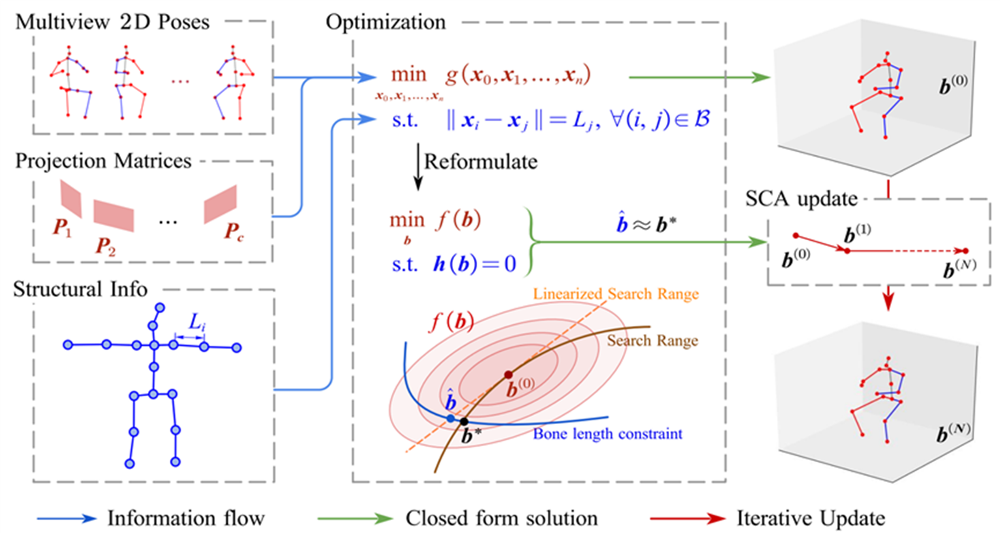
We propose Structural Triangulation, a closed-form solution for optimal 3D human pose considering multi-view 2D pose estimations, calibrated camera parameters, and bone lengths. To start with, we focus on embedding structural constraints of human body in the process of 2D-to-3D inference using triangulation. Assume bone lengths are known in prior, then the inference process is formulated as a constrained optimization problem. By proper approximation, the closed-form solution to this problem is achieved. Further, we generalize our method with Step Constraint Algorithm to help converge when large error occurs in 2D estimations. In experiment, public datasets (Human3.6M and Total Capture) and synthesized data are used for evaluation. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on Human3.6M Dataset when bone lengths are known and competitive results when they are not. The generality and efficiency of our method are also demonstrated.
Video
Highlights
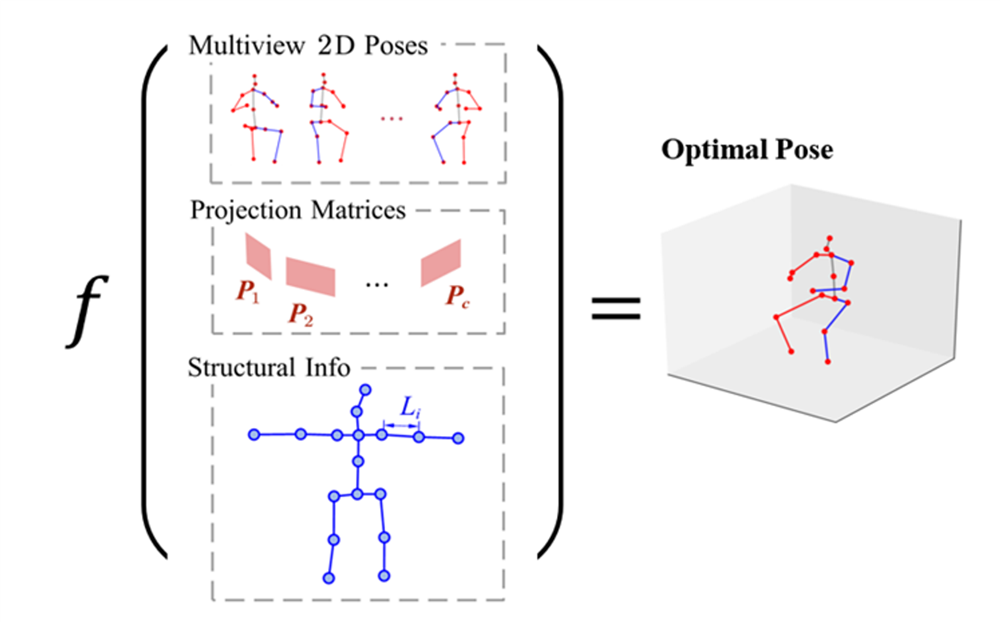
Closed Form Solution
We derive an explicit function that produces the optimal pose given multi-view 2D pose estimation, camera projection matrices, and structural information (bone lengths). The function is derived from solving a constrained optimization problem by applying an approximation (from Neumann Lemma).
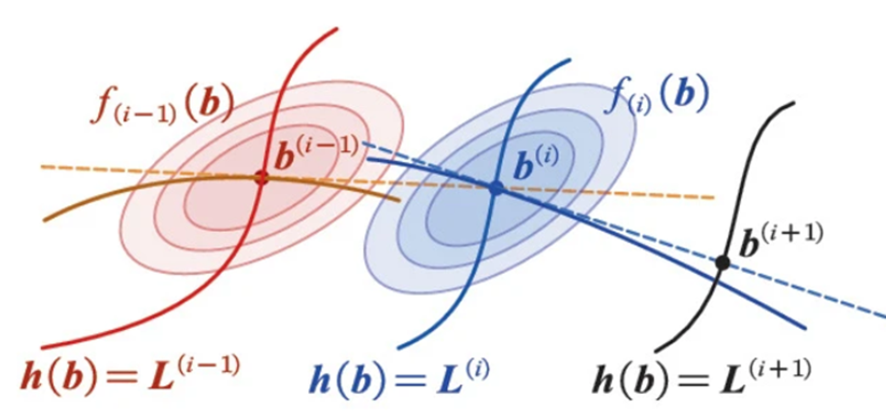
Step Constraint Algorithm (SCA)
By applying approximation, we have assumed that the initial human pose guess from SVD triangulation nearly satisfies the bone length constraint. When the assumption does not hold, we propose SCA to satisfy the constraint step by step. Proposed for our case though, SCA is applicable for generic constrained quadratic optimization problems.
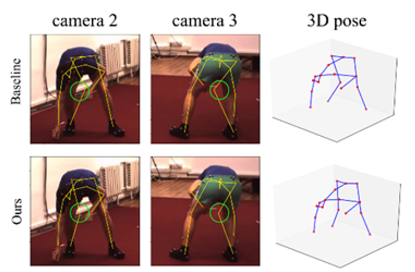
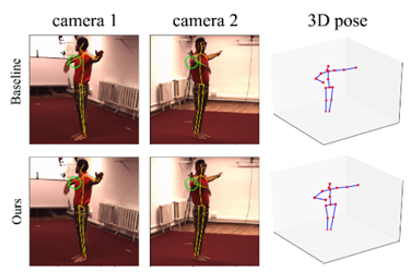
Experiments
Citation
@inproceedings{Chen2022Structural,
title={Structural Triangulation: A Closed-Form Solution to Constrained 3D Human Pose Estimation},
author={Chen, Zhuo; Zhao, Xu and Wan, Xiaoyue},
booktitle={Computer Vision – ECCV 2022},
year={2022},
}

